An Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system allows a company to set up an auto-attendant to answer calls and redirect them based on the caller’s input. This system plays a pre-recorded message that asks the caller to press certain buttons on their phone to be directed to the appropriate department or person. The IVR then routes the call accordingly.
Key Benefits of an IVR System:
- Efficient Call Handling: An IVR automates the call answering process, reducing the need for staff to manually answer and redirect calls while managing a large volume of calls simultaneously to reduce wait times and ensure callers are directed to the right department quickly.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: IVR systems provide a clear and organized menu, improving the caller experience by allowing them to reach their desired destination without unnecessary delays.
How to setup an IVR
Follow these steps to set up an IVR system to route incoming calls via an auto attendant.
- Navigate to the IVR Module
- In the main menu, go to PBX > Incoming Calls > IVR.
- Configure the GENERAL Tab
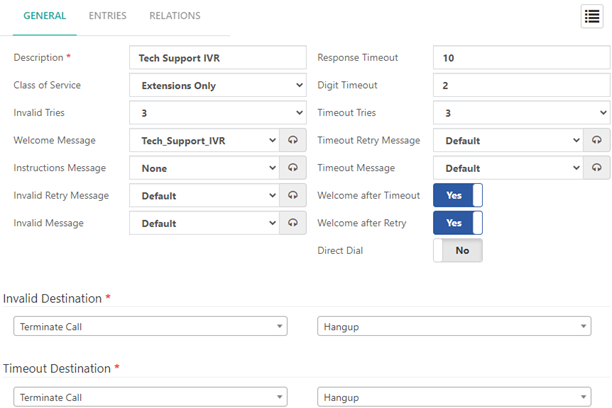
- Description: Enter a free-text description to identify this IVR.
- Configure additional IVR settings, which will use default values when creating a new IVR:
- Class of Service (CoS): Choose a Class of Service for this IVR. In the default “Extensions Only” CoS, the caller will only be able to dial internal extension numbers, preventing potential misuse of the IVR for making external calls that could incur charges. Be cautious when allowing calls beyond internal extensions to avoid unauthorized external calls.
- Invalid Tries: Specify the number of invalid attempts allowed. This setting is useful when a caller doesn’t understand the recording or makes multiple mistakes entering their input. After the specified number of invalid attempts, the caller will be sent to the Invalid Destination.
- Timeout Tries: Determines the number of times the IVR will repeat the message when no valid input is received. After the specified number of attempts, the caller will be sent to the Timeout Destination. NOTE that Limiting the number of attempts can help prevent automated systems or machines from congesting the PBX with repeated attempts.
- Direct Dial: Enable this option to allow the caller to call an extension directly from the IVR. However, please note that the ability to dial extensions directly is subject to the CoS configured for the IVR. Adjust CoS settings carefully to control which extensions callers can access directly.
3. Configure the IVR Messages:
-
- Welcome Message: Select a greeting message that plays when the caller first enters the IVR. This message welcomes the caller and provides initial instructions for navigating the menu.
- Instructions Message: Choose an instructional message that guides the caller on how to navigate through the IVR menu. This message helps users understand their options and how to proceed within the IVR.
- Invalid Retry Message: Select a message to play when the caller enters an invalid option during IVR navigation.
- Invalid Message: Select a message to be played when the caller exceeds the allowed number of attempts with invalid inputs.
- Timeout Retry Message: Select a message to be played when input has not been received within the defined timeout period.
- Timeout Message: Choose a message to be played when reaching the timeout.
- Configure any other optional settings as needed (e.g., Timeout, Digit Timeout, Timeout Tries, Timeout Retry Message, Timeout Message, Message on Timeout, Message on Invalid)
- NOTE: To manage your messages for the IVR, navigate to SETTINGS > PBX Settings > Recordings Management, as is described in the How to upload your recordings
Additionally, you can record messages directly from any phone on the system by dialing *92 (Custom Recording). Just dial *92 and follow the prompts to record your message. This option simplifies the management of IVR messages, allowing you to make quick changes without the need to upload the recording from a computer.
4. Configure the Timeout Destination and Invalid Destination (Both Required for the IVR)
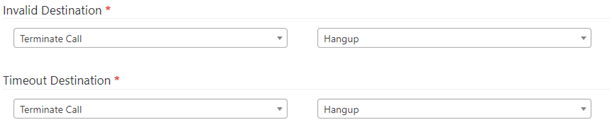
For Invalid Destination as for Invalid Destination, set these fields:
- Select Module: Choose from a dropdown list of available options to determine how calls are handled for invalid destinations.
- Select Destination: Define the call target to route when the IVR receives an invalid option.
- NOTE: To ensure optimal IVR functionality, configure both the Timeout and Invalid Destination sections. This will enhance the user experience, control system flow, and minimize errors:
Invalid Destination: This feature helps minimize user frustration by providing an alternative action after a set number of Invalid Tries. You can configure the Invalid Destination to route the call to an agent trained to handle complex situations, play an informative message explaining valid options, or offer a callback option.
Timeout Destination: This feature directs callers to a designated destination if they don’t make a selection within a predefined Response Timeout. This prevents users from getting stuck in an endless loop and discourages automated systems or machines from repeatedly tying up the PBX. You can configure the Timeout Destination to route the call to a voicemail box for example.
5. Configure the ENTRIES Tab
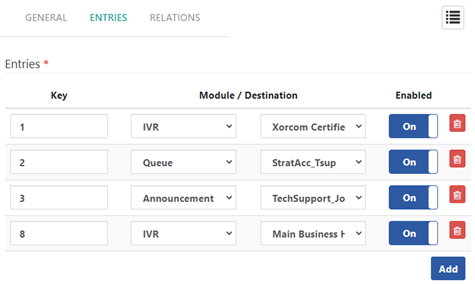
Entries Section (Required): Here’s how to handle user input:
- Key: Enter the digit (0-9) or symbols *, # on the keypad for the Module / Destination.
- Module: Select the destination type activated when the caller presses the corresponding key.
- Destination: Specify where the call will go when the caller presses the assigned digit.
- Enabled: Choose “On” to enable or “Off” to disable the key.
- Add: Press this button to add a new entry.
Note: ensure users can easily return to the previous menu:
- As a good practice, set the asterisk key (“*”) to link back to the parent IVR. This allows users to navigate back to the previous menu seamlessly.
6. Finally, you can navigate to the RELATIONS tab. This tab will give you an immediate overview of all modules associated with the selected IVR.
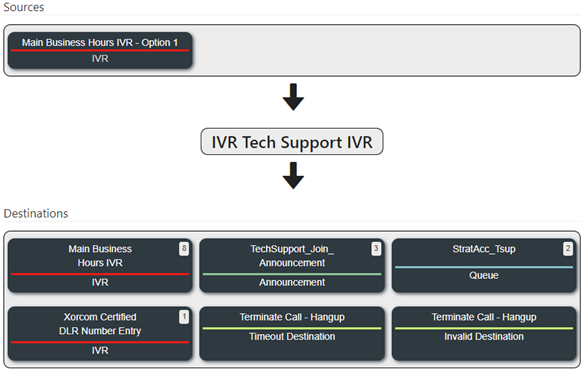
Example: Setting up an IVR for Tech Support
This example will guide you through setting up an IVR system tailored for technical support, enabling callers to reach the appropriate technical assistance quickly and efficiently.
- Navigate to the IVR Module
- Go to PBX > Incoming Calls > IVR in the main menu.
- Configure the GENERAL Tab

- Description: Enter “Tech Support IVR” to identify this IVR.
- Class of Service (CoS): Choose a CoS that allows access to technical support extensions only. In this example, the CoS is “Tech Support IVR CoS”
- Invalid Tries: Set to 3 to allow three attempts for invalid inputs.
- Timeout Tries: Set to 2 to repeat the message twice if no input is received.
- Direct Dial: Enable to allow callers to dial extensions directly (subject to CoS restrictions).
3. Configure the IVR Messages
In this example, we uploaded recorded messages for Welcome and Instruction messages by navigating to SETTINGS > PBX Settings > Recordings Management, as described in the “How to upload your recordings” section.
- Welcome Message: Select the “Tech_Support_IVR” greeting message for welcoming callers to tech support and providing initial instructions.
- Instructions Message: Select the “AH_SupportCall” message to guide callers on how to navigate the IVR menu for technical assistance.
- Leave the rest of the messages set to default; this will play default messages to handle invalid inputs and timeouts.
4. Configure the Timeout Destination and Invalid Destination
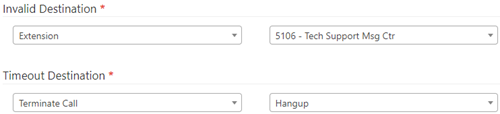
- Invalid Destination: Route calls to tech support agents trained for general issues.
- Timeout Destination: Route calls to terminate the call and hang up.
5. Configure the ENTRIES Tab
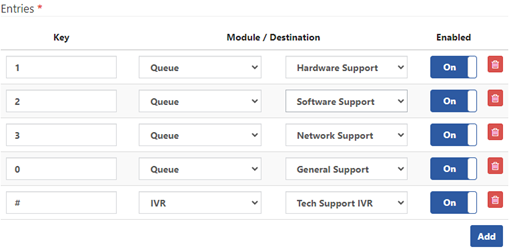
- Entries Section: Define key mappings and destinations for tech support options.
- 1 (Hardware Support): Route to the hardware support team queue.
- 2 (Software Support): Route to the software support team queue.
- 3 (Network Support): Route to the network support team queue.
- 0 (General Support): Route to the general technical support queue.
- # (Repeat): Replay the IVR menu.
6. Click the Save button to apply all configurations.
This structured setup ensures callers efficiently reach the appropriate technical support personnel, enhancing overall customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
How to upload your recordings
Follow these steps to manage your messages for the IVR.
- Navigate to the IVR Module
- In the main menu, go to SETTINGS > PBX Settings > Recordings Management.
- Upload a Sound File
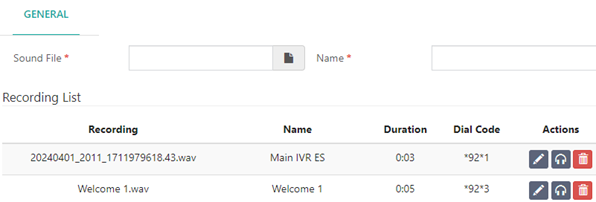
- NOTE: Each saved recording will be allocated a Dial Code, consisting of the feature code used to make recordings (typically, *92) followed by a unique identifier. Dialing this Dial Code will allow you to replace an existing recording. For example, if you uploaded a “Welcome Message” and the Dial Code is *92*4, you can dial this code to quickly replace the recording with a new one made directly from the phone call.
3. Manage Existing Recordings
- In the Recording List section, you will see all uploaded recordings where you can:
- Edit: To change the name of a recording, use the edit icon
 .
. - Play: To listen to the recording, use the headphones icon
 .
. - Delete: To delete a recording, use the trash can icon
 . Be careful, as this action cannot be undone.
. Be careful, as this action cannot be undone.
4. Assign Recordings to IVR by navigating to PBX > Incoming Calls > IVR.
- In the IVR GENERAL Tab, select the appropriate recording from the drop-down menu of pre-recorded messages for the messages options: Welcome Message, Instructions Message Invalid Retry Message, etc. NOTE that the recordings you have uploaded via the Recordings Management Module will appear in these drop-down menus.
