RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) authentication is relevant for enhancing security and centralized management of user credentials in VoIP systems like CPBX5. RADIUS allows organizations to:
- Centralize user management: All credentials and access policies are managed from a central RADIUS server, simplifying administration.
- Enhance security: Uses secure protocols for authentication, ensuring that credentials are not transmitted in plain text.
- Audit and control: Provides detailed logs of authentications and access, allowing for audits and security analysis.
How to Set Up RADIUS Authentication in CPBX5
- Navigate to the Authentication module.
- In the main menu, go to ADMIN > Security > Authentication.
- Configure the RADIUS tab.
- Select the password type which define the encoding method between:
- PAP: Transmits username and password in plain text.
- CHAP: Uses a challenge-response mechanism for authentication.
- MSCHAP v1: A version of CHAP developed by Microsoft, primarily used in Windows networks.
- EAP-MSCHAP v2: An authentication method that combines EAP with MSCHAP v2.
- Configure the User/Group VSA, Vendor ID, and Role VSA. You can leave the default parameters.
- Add the RADIUS server.
- Click on the “Add RADIUS Server” button. A dialog will appear for setting up the RADIUS server parameters:
- Enter a meaningful name for the server.
- Configure the IP address and secret of your RADIUS server (e.g., RADIUS Server). For the IP address, you can also define the port number (e.g., 10.0.0.1:9000).
- Set the timeout and number of authentication attempts for the server.
- Click the Save button to apply the changes.
- Select the RADIUS authentication in the GENERAL tab of the Authentication module.
- You can select the RADIUS authentication as the first, second or third method for login into CPBX5.
- Click the Save button to apply the changes.
- Test User Authentication:
- Attempt to log in to CPBX 5 with a user configured for RADIUS authentication.
- Verify that authentication is successful and access is granted.
Example: Setting Up RADIUS Authentication for CPBX5
In this example, we configure RADIUS authentication for CPBX5 using a FreeRADIUS server. The FreeRADIUS server is configured to manage user credentials and authenticate logins to CPBX5. Follow these steps to set up and test the RADIUS authentication.
Step 1: Navigate to the Authentication Module
- In the main menu of CPBX5, go to ADMIN > Security > Authentication.
Step 2: Add a RADIUS Server
- Click on the “Add RADIUS Server” button. A dialog will appear for setting up the RADIUS server parameters.
Step 3: Configure the RADIUS Server
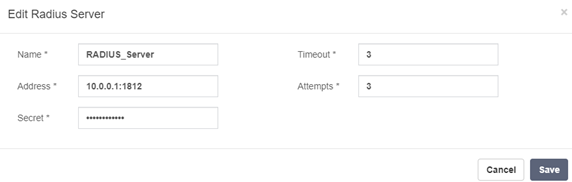
- Name: Enter a meaningful name for the server. For this example, we used “RADIUS_Server”.
- Address: Enter the IP address and port number of your RADIUS server. For example, 0.0.1:1812.
- Secret: Enter the shared secret for your RADIUS server. This must match the secret configured on the RADIUS server.
- Timeout: Set the timeout in seconds before giving up. For this example, use the default value of 3.
- Attempts: Set the number of attempts before giving up. For this example, use the default value of 3.
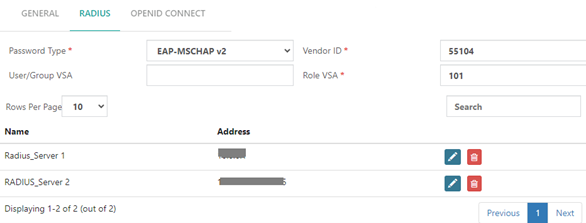
Step 4: Configure the RADIUS Parameters
- Password Type: Select the encoding method for the password. For this example, we selected EAP-MSCHAP v2.
- User/Group VSA: Set this to the value that will be submitted to each RADIUS server as vendor-specific attribute 102, e.g. admin.
- Vendor ID: Enter the vendor-specific ID, which defaults to 55104.
- Role VSA: Enter the vendor-specific attribute the PBX will use as the user role, which defaults to 101.
NOTE: You can leave these parameters at their default values unless specified otherwise by your RADIUS server configuration. Additionally, you can configure more than one RADIUS server. This allows for redundancy and failover capabilities, ensuring continuous authentication services even if one server becomes unavailable.
Step 5: Select the RADIUS Authentication in the GENERAL Tab
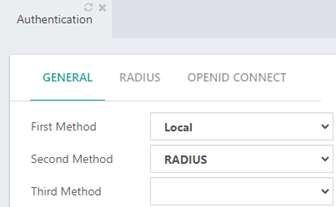
- In the GENERAL tab of the Authentication module, you can select the RADIUS authentication as the first, second, or third method for login into CPBX5. In this example, we have setup the RADIUS authentication as the second method.
- Confirm the configuration by selecting the desired authentication method. If RADIUS is the only selected method, a prompt may appear to confirm this unique setup.

- Click the Save button to apply the changes.
Step 6: Test User Authentication
- Log in to CPBX5 with a user configured on your RADIUS server. In this example, we used “bob” as the username and the corresponding secret to authenticate to CPBX5 via the configured RADIUS server.
- To verify which user logged in to CPBX5, you can check the audit log file by following these steps:
- Go to ADMIN > Maintenance > Diagnostics.
- In the GENERAL section, click the Diagnostic Mode This will put the CPBX5 system into Diagnostic Mode for a limited time.
NOTE: Running the Diagnostic Mode may affect system performance and, in case of system overload, may impact calls. - Click the option to activate Diagnostic Mode. The system will start gathering information and enter Diagnostic Mode for 10 minutes. You can also manually stop it by clicking the Stop and Download
When stopping Diagnostic Mode, or when it stops after the designated time, detailed files will be downloaded compressed as a zip file.
- Check the Audit Log File:
- Unzip the downloaded file and check the audit log file, which is named using a specific format that includes the word “audit” followed by a timestamp. For example, audit_20240730_132906.
- Look for entries related to the login Relevant log entries will have a format similar to the following:
{“time”:”2024-07-30T13:28:42+00:00″,”category”:”SECURITY”,”event”:”login“,”severity”:”Info”,”user”:”bob“,”host”:”181.199.60.93″}
{“time”:”2024-07-30T13:28:43+00:00″,”category”:”NAVIGATION”,”event”:”backup-restore-status”,”severity”:”Info”,”user”:”bob“,”host”:”181.199.60.93″}
{“time”:”2024-07-30T13:28:49+00:00″,”category”:”NAVIGATION”,”event”:”diagnostics”,”severity”:”Info”,”user”:”bob“,”host”:”181.199.60.93″}
Explanation of the Log Entries:
- Time: Timestamp of when the event occurred.
- Category: Type of event (e.g., SECURITY).
- Event: Specific action taken (e.g., login).
- Severity: Importance level of the event (e.g., Info).
- User: Username of the individual who performed the action (e.g., RADIUS user such as “bob”).
- Host: IP address of the user’s device.
NOTE: To access the audit log file directly from the system, you can connect to the PBX via SSH using a program like PuTTY and navigate to /var/log/cpbx/audit.log. The contents of this file are the same as presented in the example audit log above.
